The more you learn about search engine optimization (SEO), the more intrigued you’ll be with its constant evolution. Because SEO is always changing, you have to keep up with the latest updates of two of its biggest strategies. These strategies can be classified as either on-page SEO or off-page SEO. Let’s begin by defining each one; on-page SEO categorizes any internal aspects of your site that can be optimized, where as off-page SEO focuses on external techniques that drive traffic to your site. Now that we have an understanding of what they are, let’s get into more details.
On-Page SEO and Off-Page SEO: What’s the difference really?
On-Page SEO
A good way of thinking about on-page SEO is by focusing on things that are on your page, like content and the code used to create your page. Let’s dive a little deeper into on-page SEO.
Meta Data
In technical terms, meta data is used to describe other data. So in the SEO world, meta data is used to describe a page’s content. This descriptive snippet is coded into your page and it is meant for the use of search engine crawl bots so that they know what your page is about.
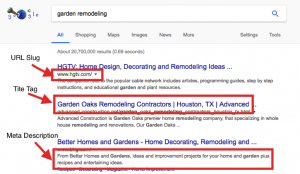
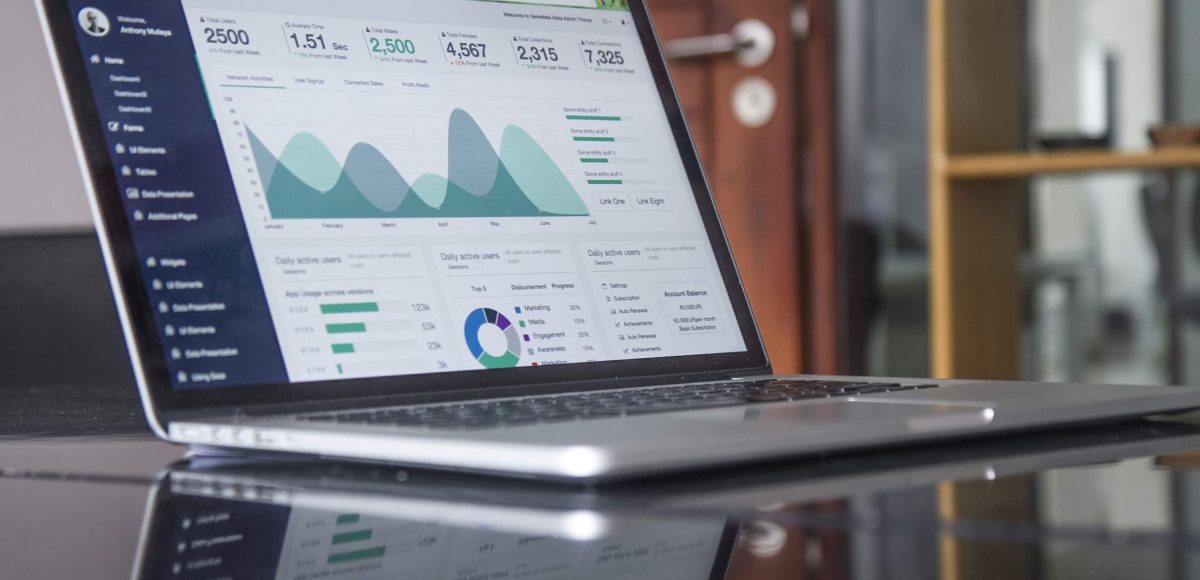
Meta Description
Since this happens to be a deciding factor for search engine users, make sure your meta description is catchy and embodies what your page is truly about. You don’t want it to be longer than 160 characters since search engines will shorten your description snippet. A healthy range of 155 is where you’d want to shoot; it’s better to be safe than sorry. A great strategy is to incorporate a call to action or any offers your site is running, you want to entice the user so let them know why your service/product is the one they should take a second look at. Lastly, don’t let your meta description be stagnant, change it up and test out different descriptions to see which ones drive more traffic to your site.
Title Tag
In simpler terms, the title tag is the title of your web page. Since it’s the most eye-catching part of the meta-data, make sure your title accurately describes the content of your page. Although you can have a lengthy title, a good rule of thumb is to keep it under 60 characters so it’s displayed completely. You want to make sure that each title tag for each individual page is distinct, duplicate titles will get you a message from Google in your Search Console account. Lastly, avoid keyword stuffing. The goal is to make the title useful so that users can make an educated decision on what page to visit, stuffing your title tag with your choice of keyword will not bode well for your page rank so don’t even bother with it.
URL Slug
Keeping the URL slug as simple as possible is key here. If your URL can’t be read and understood by a human being, as well as a search engine, then you’re in trouble. Make sure to include your keyword in the URL and if you need to separate words, use hyphens instead of underscores.
Heading Tag
When organizing your content, heading tags are quite useful in constructing your page. They come in a variety of six: H1-H6, though you are most likely not going to use all of them. The heading tag is a more “user-friendly” element, as its impact on your page rank might not be of the highest form. Although heading tags might not take you to the number one spot in a Google search, they are considerably impactful to the way your content is structured so don’t skimp out on them.
Content
There is no question that content is the most critical factor of SEO. Great content can make or break your site, so spend as much time as you can developing quality content. Google likes lengthy posts, so try to write content that is longer than 300 words. User wise, break up you posts with some white space and use bullet points when you can. Keep in mind that the more unique and useful your content is, the easier it will be to rank as it makes it shareable and fresh. Also, keep posting and updating your content in a consistent manner, as this signals to search engines that you are an active site and this equates to more indexing of your site. Lastly, updated content keeps your audience informed and increases the chances of converting new visitors to returning visitors.
Internal and Outbound Links
The art of linking is definitely important for SEO. You want to include links in your content that are related to the topic being addressed and you want these links to be trusted or “authoritative”. Think of links as “recommendations” for your page, the higher the quality, the more trusted your page becomes. When choosing what internal links to include on your page, choose links that make the sense for the user experience. Don’t over stuff your page with links for pages that you would like people to visit, as that’s something Google can see through. Outbound links should compliment your content and should come from authoritative sites, the better the “recommendation”, the higher your chances are of getting in to the top search spots. A good rule of thumb is having about 2-3 links of each for every 1000 words.
Images
Visuals are important, the better your site looks and the nicer the images you use are, the more engaged your visitors will be. Here are a few useful tips:
- Make sure to pick an image that is related to your page and/or post topic. Nothing is more annoying than reading an article on best tax practices and having a monkey wearing a party hat plopped in the middle of it.
- Name your image accordingly. Use you keyword in the file name, but don’t overdo it and stuff your keyword in it 10 times.
- Size the image to better fit your site. The correct size will not only look good, but will not impede in the page load time.
- Don’t forget to use alt text. If your image can’t be displayed, alt text is used in its place. Search engine crawl bots also use alt text, as they help translate what the image is about. Like the file name, include your keyword in the alt text of your image.
Mobile
With the rise of mobile use, your site has to cater to the mobile and tablet user now more than ever. With numbers expected to rise, smartphone users are taking over the Internet market. Make sure your site is mobile friendly, as a desktop layout does not always translate properly. Moz does a good job in giving a thorough description on how to optimize for mobile.
Site Speed
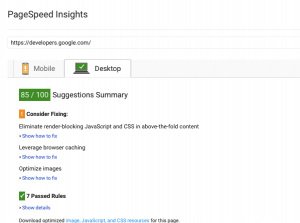
When it comes to site speed, or page speed, the faster the better. People have an 8 second attention span, so if your webpage is taking longer to load then you will not make a good impression on your users or Google. In fact, we are so impatient that if a page takes longer than 7 seconds to load, we move on to the next option. As if that wasn’t deterrent enough, the slower your page is, the longer it takes for search engine bots to crawl your site. So it’s no wonder that page speed affects your page rank. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to analyze your page speed, and make sure to check out the PageSpeed Insights Rules for a more detailed guide for increasing your page speed.
Off-Page SEO
Back Linking
In order for your site to get “authority”, you have to have more reputable sites link back to you. The more authoritative the site, the more “link juice” is filtered to your page. This can be a tall order, but if done right, you will see a substantial increase in traffic and rank. A couple of strategies that have proven to work well in the past is guest posting and utilizing industry contacts to link back to your site. Guest posting in the correct niche, a.k.a posting in blogs related to your industry, will get the desired traffic to your site. Posting in popular sites that have nothing to do with your content will not have as big of an impact and might increase your bounce rate. Utilizing industry contacts can be beneficial to both of you, as you can work together in creative cohesive linking that will cater your customer’s needs.
Social Media
Social media has become a huge part in our daily lives, so it’s not surprising that it’s making a large impact on today’s SEO atmosphere. When you Google a company, you will now see its social media accounts in search results; you can go even further and see popular or “viral” social media posts rank in search engine results. Social media platforms have adopted a “search” function that allows users to look for content they’re interested in, giving companies and brands more reason to increase their social media presence. The potential to reach large audiences and boost content distribution have made social media a sharing powerhouse, making it an increasingly important part of organic traffic.
SEO is a very technical art, you have to be able to read code to decipher what can be optimized so your site is as user friendly as possible. We will touch base on technical SEO in more blog posts.